Ahmanson Hall of the Sky

The Sun, the Moon, and the Earth
The Ahmanson Hall of the Eye reveals how the Sun and Moon interact with Earth to shape the way our planet works.
Imagine a world without day or night, with no change of seasons or annual cycles. It wouldn’t be Earth, because the Sun and Moon dominate our sky and measure the march of time. Sunrise, sunset, and the passing of years and seasons – as well as the restless tides, monthly Moon phases, and awe-inspiring eclipses – occur because the Earth and Moon move in relation to the Sun and each other. The Sun is the most dynamic object in the sky. It warms our planet and makes life possible. As the closest star to Earth, it also offers us a glimpse into the nature of all stars.

Explore the Ahmanson Hall of the Sky
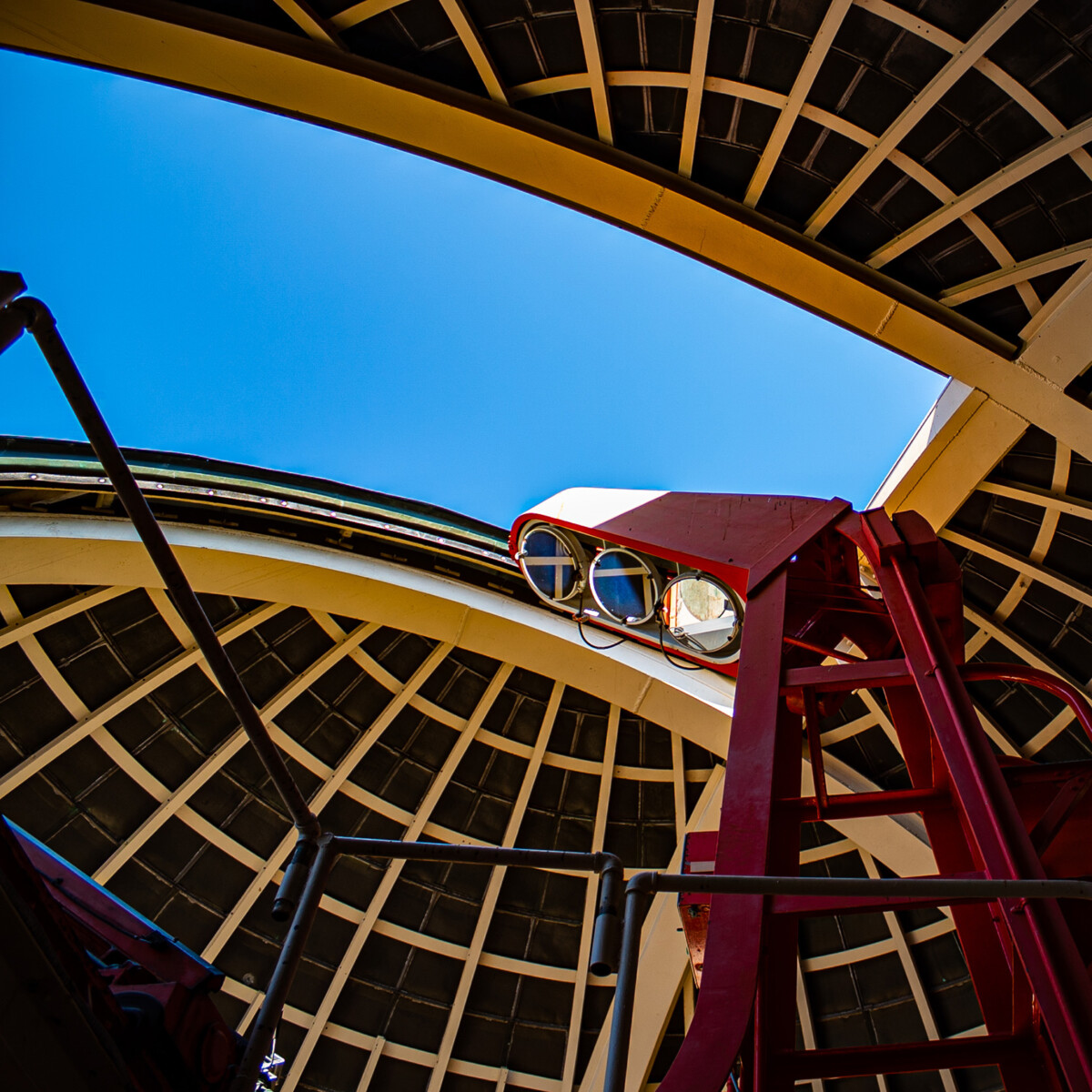

Solar Telescope Instruments (Coelostat)
Griffith Observatory’s triple-beam solar telescope brings three columns of sunlight into instruments in the west rotunda of the Ahmanson Hall of the Sky. On clear days, each of these telescopes provides a different real-time view of our local star, including sunspots, solar flares, and spectra.

Day & Night
Day and night are the most basic divisions of time. At any moment, half the planet faces the Sun and experiences day. The other half faces away from the Sun and experiences night.

Sun & Stars Paths
Every day, the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars appear to rise in the east and set in the west. Actually, these celestial objects aren't moving that fast, but Earth is. It spins on its axis from west to east approximately every 24 hours.

Seasons
Earth experiences four seasons: spring, summer, fall, and winter. This happens because our planet is tipped on its axis and the two poles point to the same directions in space all year.

Moon Phases
It is not very often we can watch the phases of the Moon change in a few minutes, as they do here overhead. In the real world you notice the shape of the Moon changing over the course of a few weeks.

Tides
The gravity of the Moon and Sun tugs on Earth, causing tidal bulges in the oceans. As Earth rotates through these bulges, we experience high and low tides.

Eclipses
Eclipses are astronomical spectacles that happen when one celestial object moves into the shadow of another. We witness these awe-inspiring events during precise alignments of the Sun, Earth, and Moon.

Our Sun is a Star
The Sun is the most important star in our sky. It lies nearby and sustains us with its light and heat. Because it is so close, we can learn more about other stars just by studying its activity and properties.

Elements
Everything around us contains material that was once part of a star. The cells in our bodies, the air we breathe, and materials that make up the planets in our solar system are all linked to the stars through chemical elements.

The Active Sun
When we observe the Sun, we are looking at an active star. We measure its temperature and watch its outer atmosphere to understand how it works. The visible surface of the Sun appears to be in full boil.